Arabic
Homework Help & Tutoring
We offer an array of different online Arabic tutors, all of whom are advanced in their fields and highly qualified to instruct you.
Arabic
Arabic is not commonly chosen as a language to study in the West. To know Arabic, however, is without any doubt the key to a whole civilization. Arabic is a very widespread and rapidly growing language. It is spoken throughout the entirety of North Africa (such countries as Morocco, Tunisia, Egypt), the Arabian Peninsula (Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Kuwait), and the Middle East (Lebanon, Syria, Jordan). Arabic is one of the official languages of Israel and it is taught in Israeli schools. The number of speakers of Arabic is now close to 300 million and it keeps growing due to the high birth rate in the countries in which that language is spoken.
The cradle of Arabic is the Arabian Peninsula. When in the 7th century the religion of Islam emerged, the spread of Islam (both by peaceful and military means) soon made Arabic the official and spoken language of an immense state known as the Caliphate, stretching from Spain in the West to Afghanistan and Pakistan in the East. This is how Arabic won its positions in North Africa and the Middle East and superceded Greek, Aramaic, Coptic, Syriac and other languages previously used in the region.
In order to fully appreciate the importance of Arabic, one should know that it is not only the language spoken in many Islamic countries, it is the sacred language of Islam. Muslims believe that the Quran was given to the prophet Muhammad directly from God in Arabic. Thus, the true text of the Quran exists in Arabic only, and studying that language is part of any Muslim education. Translations of the Quran are possible, but their text does not have the sacred value of the Arabic original.
The Caliphate was a powerful, wealthy and prosperous state where sciences and arts flourished while most of Europe lived through the period of decline known as the Dark Ages. Numerous words, including scientific terms we use on a daily basis in English came from Arabic. Some examples are algebra, chemistry, almanac, average, zenith and many others.
The first step toward learning Arabic is mastering its unique alphabet. Incidentally, a number of languages other than Arabic use the same alphabet, such as Farsi and Persian in Iran, Urdu in Pakistan and Pashto in Afghanistan. As Hebrew is, Arabic is written down from right to left. Learning the alphabet may be a bit demanding, as the letters may change their form depending on whether they appear in the beginning, in the middle, or at the end of a word, or as isolated letters. Take a look at the following table (taken from Omniglot) to get an idea of how Arabic letters change:
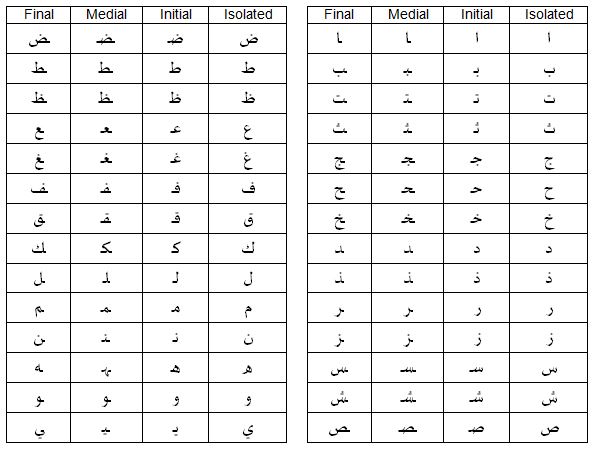
This website, designed by the Arabic Department of the Stanford University, will be of much help for learning the Arabic alphabet. MyEasyArabic website is another interactive tool to aid in mastering both writing and pronunciation.
To fulfill our tutoring mission of online education, our college homework help and online tutoring centers are standing by 24/7, ready to assist college students who need homework help with all aspects of Arabic. Our languages tutors can help with all your projects, large or small, and we challenge you to find better online Arabic tutoring anywhere.
College Arabic Homework Help
Since we have tutors in all Arabic related topics, we can provide a range of different services. Our online Arabic tutors will:
- Provide specific insight for homework assignments.
- Review broad conceptual ideas and chapters.
- Simplify complex topics into digestible pieces of information.
- Answer any Arabic related questions.
- Tailor instruction to fit your style of learning.
With these capabilities, our college Arabic tutors will give you the tools you need to gain a comprehensive knowledge of Arabic you can use in future courses.
24HourAnswers Online Arabic Tutors
Our tutors are just as dedicated to your success in class as you are, so they are available around the clock to assist you with questions, homework, exam preparation and any Arabic related assignments you need extra help completing.
In addition to gaining access to highly qualified tutors, you'll also strengthen your confidence level in the classroom when you work with us. This newfound confidence will allow you to apply your Arabic knowledge in future courses and keep your education progressing smoothly.
Because our college Arabic tutors are fully remote, seeking their help is easy. Rather than spend valuable time trying to find a local Arabic tutor you can trust, just call on our tutors whenever you need them without any conflicting schedules getting in the way.




